Perform
What do I eat during my cycling training?
Prioritize carbs during your training and keep proteins and fats to a minimum. Your specific carb needs depend on the duration and intensity of your cycling training.
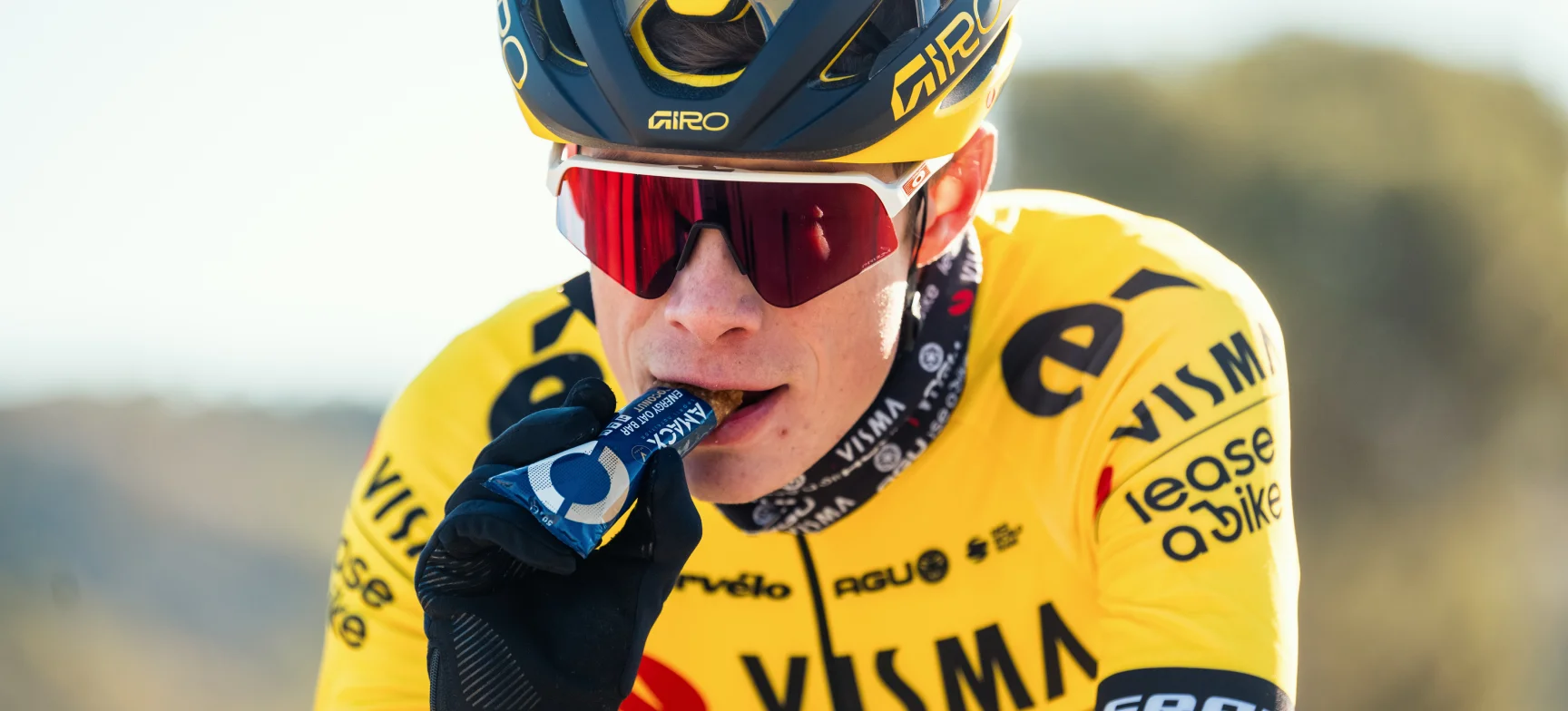

Why should I eat carbs during my cycling training?
- Maintain fuel levels: Carbs are broken down into glucose, which is used by you body for energy. Eating carbs during your training provides a continuous source of glucose to fuel your muscles.
- Maintain optimal performance: When your glycogen stores run low, your body needs to rely more on fat reserves for energy. Using fat for energy is less efficient and therefore slower. This leads to a significant drop in performance.
- Delay fatigue:The feeling of fatigue during cycling often occurs when your muscle glycogen stores become depleted. Consuming carbs provides an external source of glucose, which helps preserve your glycogen stores and keeps riding fun also in the last part of training.
- Prevent hitting the wall: When your muscle glycogen stores become depleted you can notice an abrupt loss of energy and performance, known as "bonking" or hitting the wall.
- Improved recovery: During a ride, you deplete your glycogen stores, which need to be replenished after your ride. By consuming carbs during your ride, you support the process of glycogen replenishment and facilitate muscle repair, preparing your body for your next training session.
How do I get my carb intake during cycling on point?
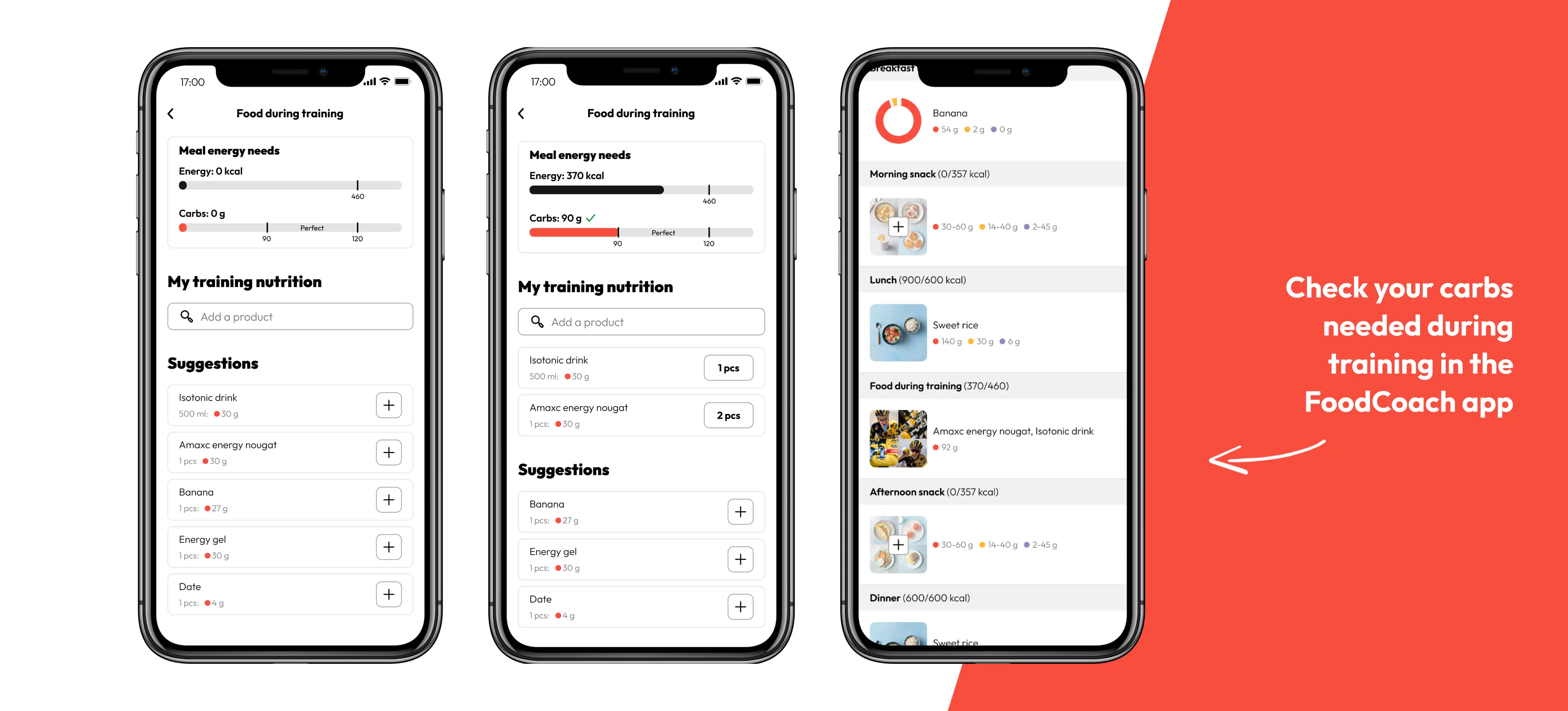
In general, aim for a minimum of 30 grams of carbs per hour when cycling over one hour. Dependent on the total duration, intensity and goal of the training, the intake can be up to 90 grams per hour or even more. Plan your training in The FoodCoach App, it will give you specific recommendations based on your ride and help you translate these recommendations into real foods.
Popular products during cycling
Read more
Definitions
- - Carbs: carbohydrates are macro-nutrients found in various forms, including sugars, starches, and dietary fiber, primarily serving the function of providing energy to the body.
- - Glucose: a simple sugar, often referred to as blood sugar, that remains when carbs are broken down and is transported in the bloodstream.
- - Glycogen: stored form of carbohydrates in the liver and muscles, serving as a readily accessible source of energy for the body during periods of high energy demand.
Improve this blog
Our blogs aim to the make world's best nutrition insights and research actionable for you.



