Protect
What is energy balance in sports nutrition?
Energy balance in sports nutrition means making sure the number of calories you eat and drink (energy in) matches the number of calories you use, during exercise, daily activities and basal metabolism (energy out). To manage your energy balance, adjust your calorie intake and expenditure to match your activity level and goals.

Why is energy balance important for athletic performance?
- Maintaining body weight: The use of nutritional Over time, reaching energy balance helps to maintaining body weight, whereas a positive energy balance leads to weight gain and a negative energy balance potentially leads to weight loss, both of which can impact performance.
- Maximize training effects: Energy balance is crucial for achieving your training goals by providing the necessary energy and supporting the intake of sufficient nutrients required for exercise performance, recovery, and training adaptation.
- Injury prevention: Proper energy balance reduces the risk of fatigue and injuries by supporting performance and recovery. It's like keeping your bike well-maintained to prevent breakdowns during the ride.
- Supports proper body function: Maintaining energy balance provides the necessary energy for essential bodily functions, including hormonal regulation, digestion, temperature control, and menstrual stability in women, all critical for health and performance
- Stronger immune system: Maintaining energy balance supports sufficient nutrient and energy intake to strengthen your immune system and making it better prepared to fend off illnesses.
- Peak performance: With the right energy balance, you'll have the energy you need to excel in your sport. It's like having a full tank ready for action, so you can train harder and compete better!
How do I get my nutritional supplements on point?
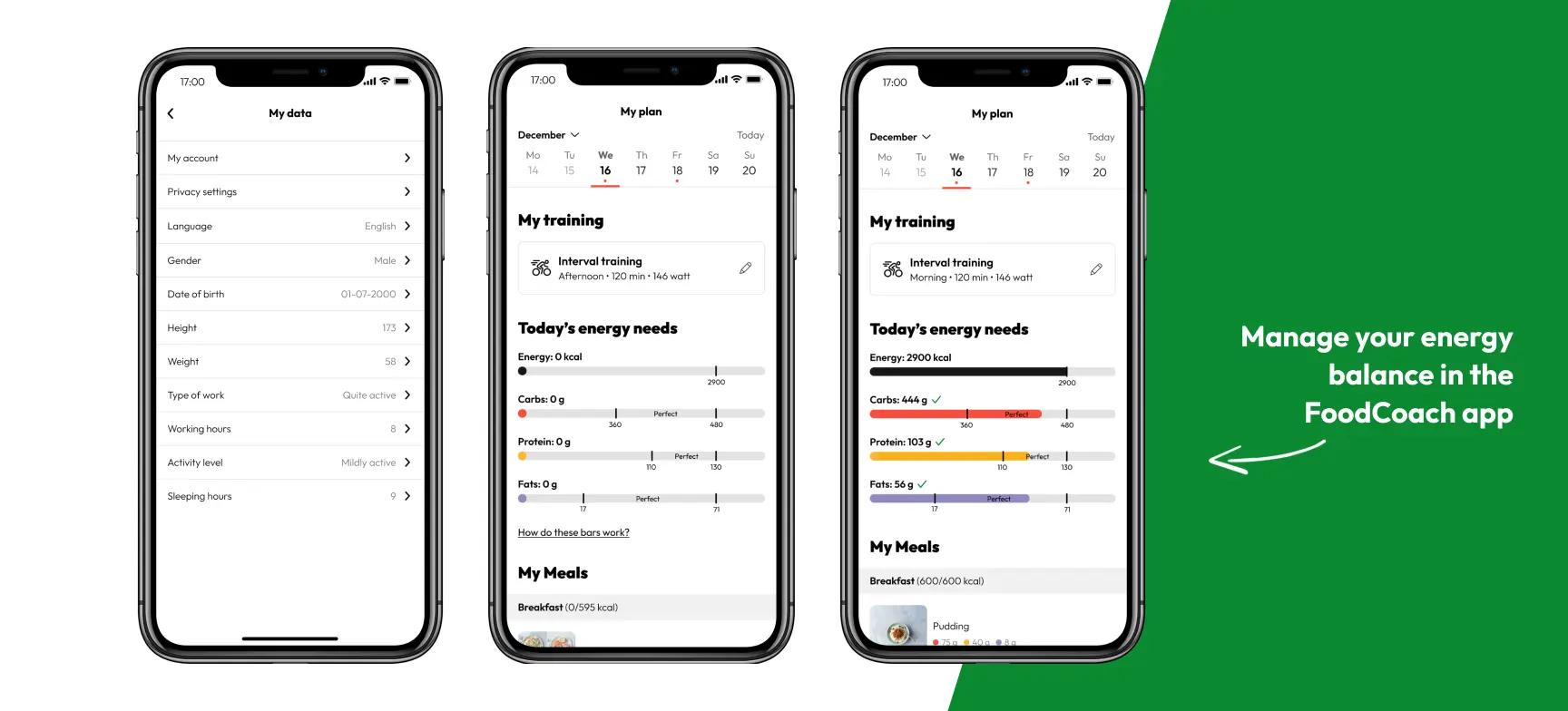
Balancing personal energy intake and -expenditure in daily life can be a complex task. Athletes need to rely on their appetite, but this can be a challenge when training intensively or when circumstances change, for instance when adjusting to a new training regime or -schedule.
The FoodCoach app simplifies this by calculating your individual energy needs, and help you translating that into practical, day-to-day nutrition choices. So you can create eating routines tailored to your new training schedule.
Read more
Definitions
- - Basal metabolism: Refers to your Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR), which represents the minimum amount of energy (in the form of calories) that your body needs to maintain basic physiological functions while at complete rest.
- - Energy: refers to the capacity of the body to perform physical work and sustain physiological functions, with energy derived primarily from the nutrients in food and drinks. It is measured in calories or joules.
- - Calorie: A calorie is a unit of measurement representing the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water by 1 degree Celsius. In nutrition a calorie is representing the energy content of food and the energy expended by the body through metabolic processes and physical activity.
- - Positive energy balance: occurs when the body's energy intake (calories consumed through food and drink) exceeds the energy expenditure (calories burned through metabolic processes and physical activity). This results in an excess of calories, which can lead to weight gain over time.
- - Negative energy balance: when the body's energy expenditure (calories burned through metabolic processes and physical activity) exceeds the energy intake (calories consumed through food and drink). This results in a calorie deficit, potentially leading to weight loss over time.
Improve this blog
Our blogs aim to the make world's best nutrition insights and research actionable for you.
